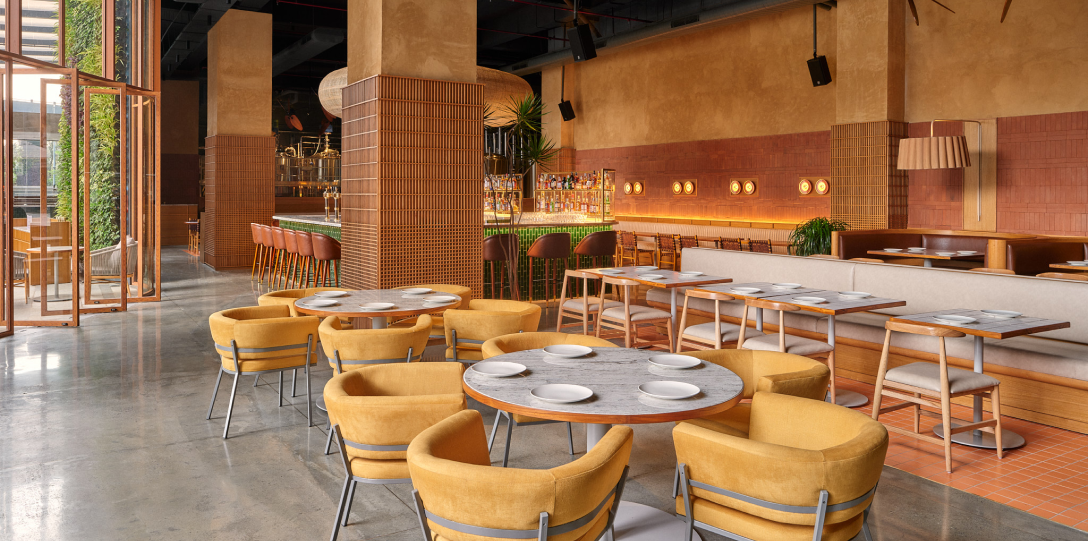
Sustainable hotel design is rapidly gaining momentum in Bangalore, as hospitality brands respond to both environmental challenges and the preferences of eco-conscious travelers. With its tech-savvy population and growing awareness of green building practices, Bangalore is emerging as a regional leader in eco-friendly interior design.
Here’s how the city’s hospitality and recreation interior design industry is embracing sustainability through innovative interior practices:
Use of Locally Sourced and Natural Materials
-
- Trends: Hotels are increasingly using bamboo, jute, reclaimed wood, terracotta tiles, and locally quarried stone.
- Impact: Reduces carbon footprint and supports regional craftspeople and economies.
- Example: Boutique hotels and eco-resorts on Bangalore’s outskirts often feature exposed laterite walls and handmade décor using natural dyes.
Energy-Efficient Interior Systems
- Adoption: LED lighting, smart thermostats, motion-sensor lights, and energy-efficient HVAC systems are becoming the norm.
- Impact: Significant reduction in electricity consumption while enhancing guest comfort.
- Highlight: Some upscale properties integrate solar energy and use interior design to optimize natural light.
Eco-Conscious Furnishings and Décor
- Sourcing: Upcycled furniture, FSC-certified wood, VOC-free paints, and organic fabrics (like hemp or linen) are gaining popularity.
- Design Philosophy: Minimalist, biophilic interiors that blur the line between indoor and outdoor spaces.
- Example: Hotels like The Green Pathintegrate recycled materials into custom-made furniture and organic bedding.
Water-Saving Fixtures and Materials
- Interior Focus: Dual-flush toilets, low-flow showerheads, water-efficient spa designs, and drought-tolerant plants in green walls or lobby spaces.
- Sustainability Strategy: Many hotels collect greywater and rainwater for internal use in landscaping or restrooms.
LEED and IGBC Certifications
- Industry Movement: Several Bangalore hotels are actively pursuing certifications like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) or IGBC (Indian Green Building Council).
- Role of Interiors: Eco-friendly materials, waste management zones, indoor air quality, and non-toxic materials are key assessment criteria.
Waste Management and Material Lifecycle
- Implementation: Designated recycling stations, composting areas, and low-waste procurement are being built into service areas and guest zones.
- Guest Engagement: Informational design (like digital signage or in-room prompts) encourages sustainable behavior.
Smart Technology Integration
- Usage: App-controlled lighting, energy dashboards in rooms, and occupancy sensors reduce unnecessary energy use.
- Sustainability Bonus: Technology supports adaptive interiors, optimizing resource use based on real-time guest behavior.
Case Examples from Bangalore
- ITC Gardenia: India’s first LEED Platinum-rated hotel, it combines luxury with green interiors, including vertical gardens and solar-powered lighting.
- The Paul Bangalore: Known for eco-conscious operations, with interiors designed around energy efficiency and low-impact materials.
Conclusion
Bangalore’s hospitality sector is blending local culture with global green standards, creating eco-friendly interiors that are both stylish and sustainable. From material selection to smart interiors, hotels are reimagining what luxury can look like in a carbon-conscious world.
Read the details on Design Arc Interiors