Environmental safety is a critical concern for communities, industries, and governments worldwide. One of the hidden risks that can impact human health and the environment is radon, a naturally occurring radioactive gas. Understanding and managing radon exposure is essential, and this is where radon flux monitoring becomes an important tool. This article explores the role of radon flux monitoring in environmental risk assessment and its significance in maintaining a safer environment.
Understanding Radon and Its Risks
Radon is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that originates from the natural decay of uranium in soil, rock, and water. While it is naturally present in the environment, elevated radon levels can pose serious health risks. Long-term exposure to high radon concentrations has been linked to lung cancer, making it a significant public health concern. Environmental risk assessment focuses on identifying and mitigating such hazards to prevent harm to humans and the ecosystem.
Radon can accumulate in enclosed spaces such as homes, schools, and workplaces, making indoor radon levels particularly concerning. Detecting radon and understanding its movement through soil and building materials is a key step in evaluating environmental risk.
What Is Radon Flux Monitoring?
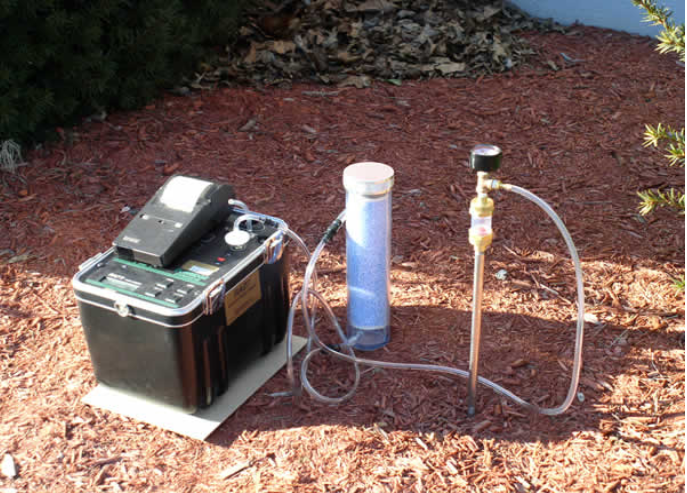
Radon flux monitoring is the process of measuring the rate at which radon gas escapes from the ground or other surfaces into the atmosphere. This measurement helps scientists understand how much radon is being released into the environment and how it may spread in air, water, or soil. Unlike general radon detection, which often focuses on indoor concentrations, radon flux monitoring examines the source and intensity of radon emission at specific locations.
By continuously monitoring radon flux, researchers can collect detailed data over time, helping to identify trends, seasonal variations, and potential hotspots. This information is crucial for creating accurate environmental risk assessments and for designing effective mitigation strategies.
Importance in Environmental Risk Assessment
Radon flux monitoring plays a vital role in environmental risk assessment for several reasons. First, it provides quantitative data that can be used to evaluate exposure levels. This helps authorities determine whether specific areas are at higher risk and need targeted intervention. Second, the data from radon flux monitoring can guide land use planning, construction practices, and public health policies. Areas with high radon emissions may require specific building designs, ventilation strategies, or other preventive measures to protect residents.
Additionally, radon flux monitoring supports regulatory compliance and environmental management. Many countries have established guidelines and safety limits for radon exposure. Continuous monitoring ensures that industries, construction projects, and residential developments adhere to these standards, minimizing potential health risks.
Methods and Techniques
There are several methods used in radon flux monitoring, ranging from simple passive detectors to advanced active monitoring systems. Passive devices, such as alpha track detectors, provide long-term measurements without requiring electricity. Active systems use electronic sensors to continuously record radon flux levels in real-time, offering detailed insight into fluctuations and peak emissions.
Field studies often combine soil sampling, meteorological data, and radon flux measurements to produce comprehensive environmental assessments. These integrated approaches help scientists understand how radon behaves under different environmental conditions and identify factors that influence its release.
Challenges in Monitoring Radon Flux
While radon flux monitoring is essential, it does face challenges. Radon emission can vary widely depending on soil type, moisture content, temperature, and atmospheric pressure. These variations can make it difficult to predict exposure levels accurately. Moreover, long-term monitoring is required to capture seasonal changes, which can increase the cost and complexity of assessments. Despite these challenges, ongoing advancements in monitoring technology are improving the reliability and accessibility of radon flux data.
Conclusion
Radon flux monitoring is a critical tool in environmental risk assessment, providing essential data to identify and manage the risks associated with radon exposure. By measuring the rate at which radon is released into the environment, scientists and authorities can make informed decisions to protect public health and the ecosystem. With continued advancements in monitoring techniques and increased awareness, radon flux monitoring will remain a cornerstone in the effort to maintain safer living and working environments. Its role in guiding policy, building practices, and public safety underscores the importance of understanding this invisible environmental threat.